Resources
Food Banking in Asia
Food banks collect food donations from a wide variety of sources and distribute them to both individuals and to welfare agencies, faith-based groups, and nonprofits that serve people in need.
Food Bank Models
- B2B: Food banks act as wholesale operations serving only welfare agencies, nonprofits, and faith-based groups how in tern serve provide direct services. In France this is the model.
- B2C: Food banks provide direct services to those in need. In the UK this is the model.
- Blended: Food banks provide food to both individuals and agencies. In the US most food banks follow this model.
Models in Asia
- Korea: Mainly B2C
- China: Mainly B2C
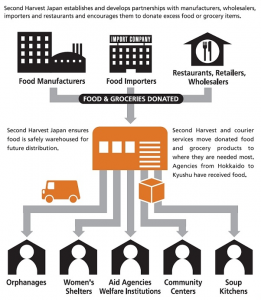
- Japan: Mainly B2B with the largest food bank, Second Harvest Japan, blended
- Taiwan: Mainly B2C
- Hong Kong: Mainly B2C
- Malaysia: Mainly B2C
- Singapore: Mainly B2C
Benefits of Working with Food Banks
For Individuals
- Reduce food waste and cost of throwing away excessive purchases
- Gain a sense of self-fulfillment from volunteering to help people in need
- Meet and make new friends with a similar social conscience
For Partner Nonprofits
- Reduce food costs and free up your resources
- Meet nutritional and emotional needs of your clients
- Opportunities to receive higher quality food
For Donor Companies
- Reduce food waste and cost of disposing overproduction or excess inventory
- Reduce impact on the environment from food waste
- Raise employee morale through employee volunteer activities at food banks
- Contribute to addressing food waste and hunger issues in your local community
- Local Government
- Reduce food loss and waste
Hunger and Food Waste
Realities in Asia
The U.N food experts estimated that 42% of fruit and vegetables and 20% of the grains produced in Asia Pacific are lost and wasted each year. Yet over 560 million people in this region suffer from hunger.
Reasons for Food Waste
- Over harvest and food waste throughout the logistical flow
- Overproduction, and product and packaging damage
- Inadequate storage
- Lack of awareness and confusion about “best before” and “use by” date labels
- Logistical and stock management inefficiencies
- Aesthetic issues with produce or packaged food
- Excess inventory
- Inadequate packaging